Flaw detection and evaluation
- Leak detection
- Location determination
- Dimensional measurements
- Structure and microstructure characterization
- Estimation of mechanical and physical properties
- Stress (strain) and dynamic response measurements
- Material sorting and chemical composition determination
Six month common NDT methods
- Visual
- Liquid penetrant
- Magnetic
- Ultrasonic
- Eddy current
- X-ray
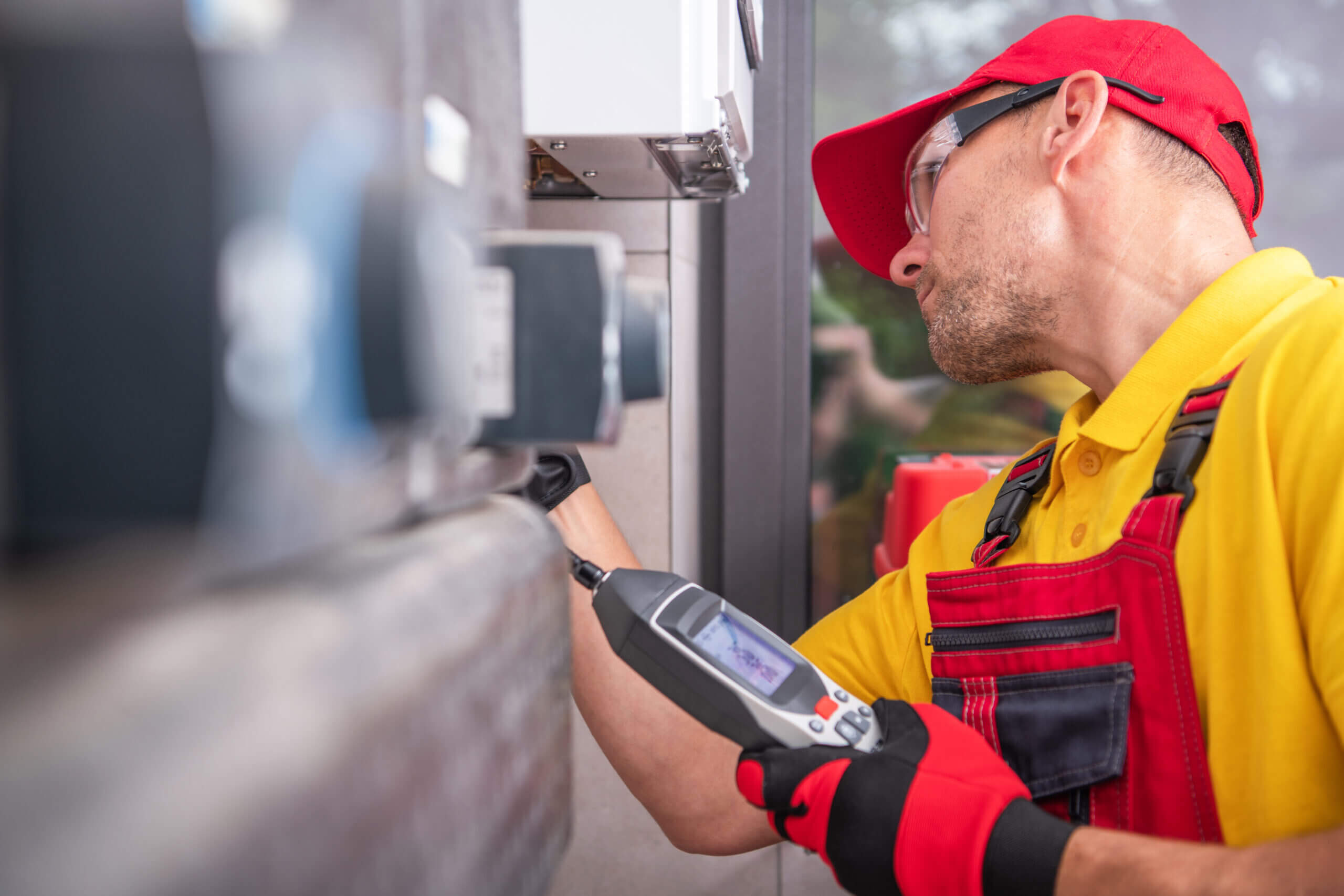

Visual inspection
- Most basic and common inspection method
- Tools include fiberscopes, bores copes, magnifying glasses and mirrors
- Portable video inspection unit with zoom allows inspection of large tanks and vessels, railroad tanks cars, sewer lines.
- Robotic crawlers permit observation in hazardous or tight areas, such as ducts, reactors, pipelines.
Magnetic particle inspection
The part is magnetized.
Finely milled iron particles coated with a dye pigment are then applied to the specimen.
These particles are attracted to magnetic flux leakage fields and will cluster to forma an indication directly over the discontinuity
Category III – The requirements assembly , inspection and cleaning required to conduct NDT of all defined critical areas. All welds
Are being visually examined and welds in critical areas should be inspected using magnetic particle or liquid penetrant method in accordance with section 6 of AWS D1.1.
Category IV – inspection should be conducted by or closely supervised by a professional engineer, original equipment.
Manufacturer representative or other manufacturer of drilling structures’ authorized representative. Category IV inspectors should Satisfy the requirements of category III inspectors and also be qualified to perform weld inspection.
Note // this type of inspection should be conducted closely or by representative of origin equipment’s manufacturer or another manufacturer of structure representative.
